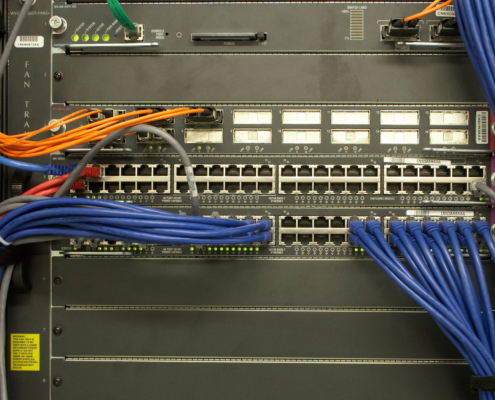
Different categories of Ethernet cables are designed to support a diverse range of data transfer rates. For instance, a Cat5e cable typically supports up to 1 Gigabit Ethernet, while a Cat6 cable can accommodate 10 Gigabit Ethernet up to 55 meters. The latest Cat8 cables even reach bandwidths up to 2000 MHz for extraordinarily fast data transfer rates. Choosing the right CAT type is a balance between current network demands and future-proofing for more data-heavy applications.
- Cat5e: Up to 1000 Mbps (1 Gbps) with a bandwidth of 100 MHz
- Cat6: Up to 10 Gbps at lengths up to 55 meters with a bandwidth of 250 MHz
- Cat6a: Up to 10 Gbps at full 100 meters with a bandwidth of 500 MHz
- Cat7: Up to 10 Gbps at 100 meters with a bandwidth of 600 MHz
- Cat8: Up to 40 Gbps up to 30 meters with a bandwidth of 2000 MHz
Figuring out when and where to employ each cable type depends largely on the specific needs of your network. Data-intensive applications such as cloud computing, video streaming services, and gaming platforms require cables with higher bandwidths to maintain optimal performance without interruptions or lag.
It’s crucial to fully assess the data transfer demands of your current and future networking projects to ensure that your cabling infrastructure can support the load. As we march into an era of ever-increasing digital consumption, selecting the right Cat cabling isn’t just an IT decision–it’s a business imperative.